Ohm's Law Calculator
Calculate voltage, current, or resistance. Enter any two values.
Theory
Ohm’s Law is one of the most fundamental principles in electrical and electronics engineering. It defines the relationship between voltage, current, and resistance in an electrical circuit and is widely used in circuit analysis, troubleshooting, and design..
This Ohm’s Law Calculator helps you quickly calculate voltage, current, resistance, or power by entering known values. It is useful for students, technicians, hobbyists, and engineers who need fast and accurate results.
What Is Ohm’s Law?
Ohm’s Law states that the current flowing through a conductor is directly proportional to the voltage applied across it, provided that the temperature and other physical conditions remain constant.
Mathematically, Ohm’s Law is expressed as:
V = I × R
Where:
• V is the voltage in volts (V)
• I is the current in amperes (A)
• R is the resistance in ohms (Ω)
This simple equation forms the foundation of most electrical calculations and is applicable to both DC circuits and AC circuits (under steady-state conditions).
Ohm’s Law Formula Variations
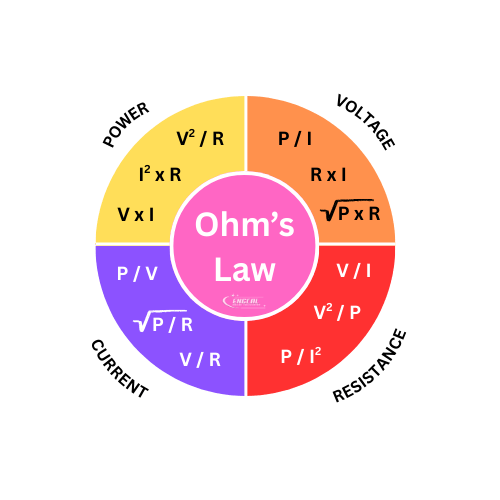
Depending on which quantity you want to calculate, Ohm’s Law can be rearranged into different forms:
• Voltage:
V = I × R
• Current:
I = V ÷ R
• Resistance:
R = V ÷ I
These formulas allow engineers to solve circuits even when only two parameters are known.
Electrical Power Calculation Using Ohm’s Law
Electrical power is another important quantity that can be calculated using Ohm’s Law relationships.
The basic power formula is:
P = V × I
By combining this with Ohm’s Law, additional power equations can be derived:
• P = I² × R
• P = V² ÷ R
Where:
• P is power in watts (W)
These equations are widely used for resistor power rating selection, thermal analysis, and energy calculations.
How to Use the Ohm’s Law Calculator
Using the calculator is simple:
1. Enter any two known values among voltage, current, resistance, or power.
2. Leave the field you want to calculate blank.
3. Click the Calculate button.
4. The calculator instantly computes the missing value using Ohm’s Law.
The calculator automatically applies the correct formula based on your input, reducing calculation errors and saving time.
Practical Applications of Ohm’s Law
Ohm’s Law is used extensively in real-world electrical and electronic systems, including:
• Designing and analyzing DC circuits
• Selecting resistor values in electronic circuits
• Calculating current draw in power supplies
• Determining power dissipation of components
• Troubleshooting faulty electrical connections
• Estimating battery life and load behavior
Because of its simplicity and reliability, Ohm’s Law is often the first concept taught in electrical engineering courses.
Limitations of Ohm’s Law
Although Ohm’s Law is extremely useful, it does have limitations:
• It applies only to linear components such as resistors
• It does not hold true for non-linear devices like diodes, transistors, or lamps
• Temperature changes can affect resistance, causing deviations
• It assumes steady-state conditions in AC circuits
For complex circuits, Ohm’s Law is combined with other laws such as Kirchhoff’s Voltage Law (KVL) and Kirchhoff’s Current Law (KCL).
Common Mistakes When Using Ohm’s Law
• Forgetting unit consistency (volts, amperes, ohms)
• Ignoring power ratings of components
• Applying Ohm’s Law directly to non-linear devices
• Confusing AC RMS values with peak values
Using a calculator helps minimize these mistakes by applying correct formulas automatically.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
Is Ohm’s Law applicable to AC circuits?
Yes, Ohm’s Law applies to AC circuits when using RMS values and considering impedance instead of pure resistance.
Can Ohm’s Law be used for power calculations?
Yes, power can be calculated using Ohm’s Law combined with basic power formulas.
Why does Ohm’s Law not work for diodes?
Diodes are non-linear devices, meaning their current does not increase proportionally with voltage.
Is Ohm’s Law still relevant in modern electronics?
Absolutely. Despite advances in electronics, Ohm’s Law remains essential for understanding circuit behavior.
